Artificial photosynthesis could be a way to generate electricity without using fossil or non-renewable energies. It is also necessary to make the process profitable in terms of energy. Thus, a team of researchers developed a way to increase the production of electricity produced by microalgae.
It is possible to produce electricity from photosynthesis!
Algae, like all plants, convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. This process takes place thanks to the presence of certain proteins, lipoproteins. The benefit of algae is that the spectrum of light they can absorb is significantly greater than the spectrum of chlorophyll in plants. Thus, the photosynthetic properties of algae have rapidly given rise to many potential applications in biotechnology. Plant proteins are also at the center of research topics on organic matter using light as an energy source.
One of the challenges of artificial photosynthesis is generating energy as efficiently as other solar-based devices. Microalgae is also used in the manufacture of some solar panels, which makes it possible to reduce the use of toxic products. However, the natural process of converting sunlight into electricity is slow. Too slow to think about marketing at scale. On average, conventional solar panels have an efficiency of 15-20%, while the efficiency of artificial photosynthesis is currently only 4.5%. However, this mechanism has the advantage of being more renewable. So there is a certain interest in progressing in this direction and improving the productivity of this vital energy.
Microalgae encapsulated to enhance electricity production
So a team of researchers from Nanyang University of Technology focused on developing a way to increase the productivity of artificial photosynthesis. The results were published in the journal ACS Applied Material Interfaces.
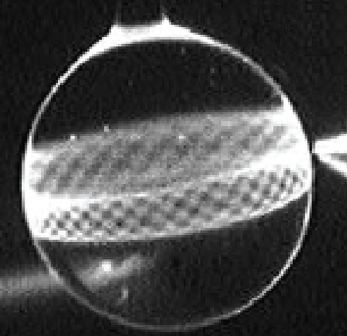
In order to amplify the amount of energy the algae can produce via photosynthesis, the team led by Chen Yu-Cheng developed a method that consists of trapping red algae inside a tiny liquid crystal droplet. The advantage of this technique is that when a tiny droplet is exposed to light, a very special optical phenomenon occurs: light waves propagate along the curved surface of the droplet. This physical phenomenon causes the light inside the drop to be captured for a longer time, allowing the photosynthesis process to run for longer and thus generating more energy.
Thus, the algae trapped inside the micro-droplet will produce energy in the form of free electrons, which are then captured with the electrodes. This technology makes it possible to produce an electric current.
By acting as a resonator, the fine droplets allow more light to be absorbed than a conventional device. One way to increase the energy production generated by microalgae and increase the energy yield of artificial photosynthesis of biomaterials is by using this process. Moreover, since the production of these droplets is easy and done at lower cost, which makes the method widely applicable in a variety of fields. For solar panels that already use algae to generate electricity, this method will produce 2 to 3 times more energy.