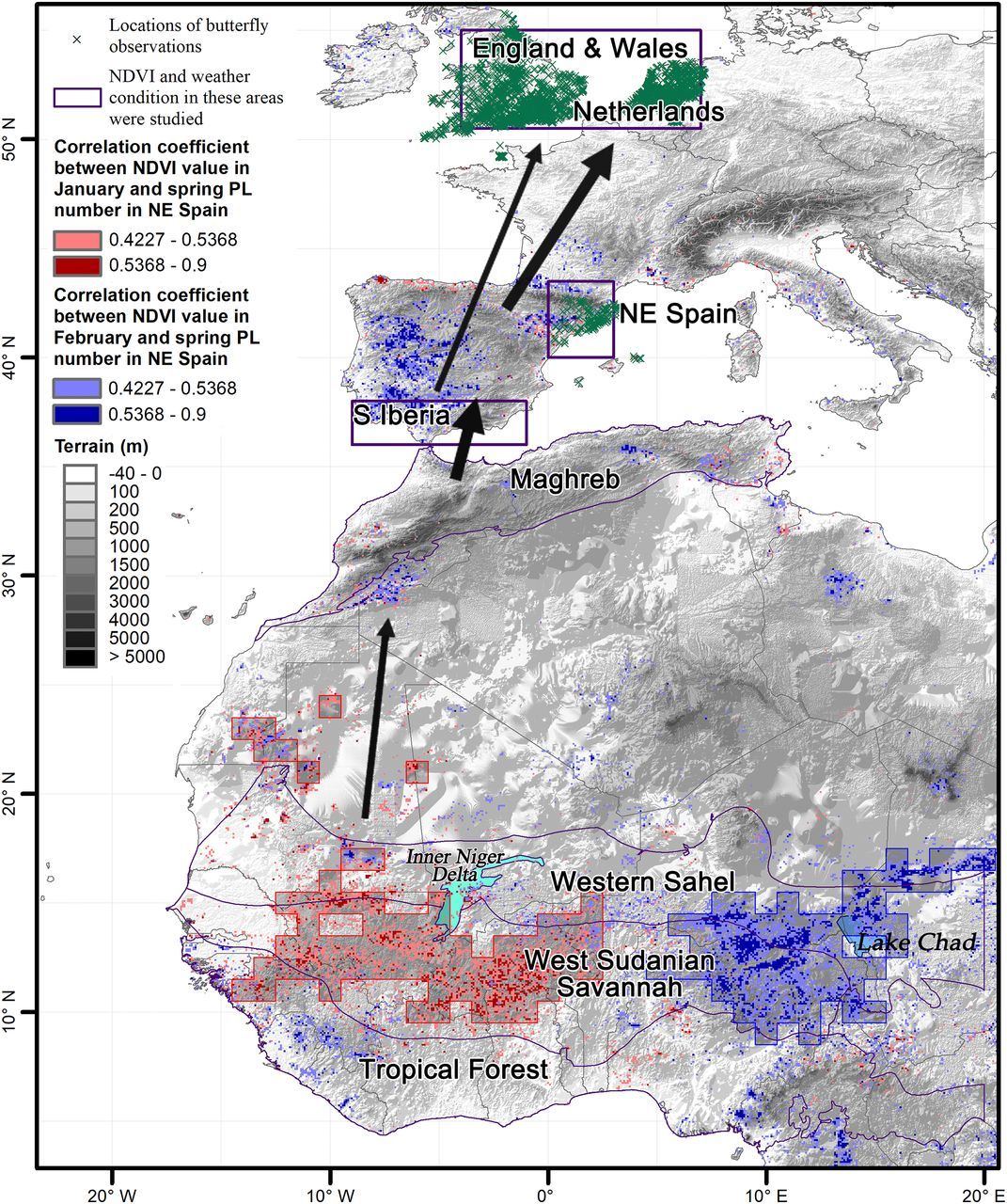
The butterfly effect has never lived up to its name. A small change in precipitation in Africa could have unexpected consequences for the populations of a species of butterfly in Europe. This is what the article published Science. The researchers say that winter rainfall in sub-Saharan Africa – which controls vegetation growth – has a significant impact on the numbers of the bells-dams moth (Vanessa Cardoy) The following summer in Europe.
La Belle-dame, a unique butterfly
With its orange and black wings, the Belle-Dame is a perfect double for the attractive Monarque butterfly. However, unlike its mostly American cousin, the Belle Dame is one of the most common butterflies in the world. It settled on almost every continent except Antarctica and South America. Its population exceeds ten million people in Europe alone.
>> To read also: “Butterflies: What is the secret of the patterns that decorate their wings?”
Another great feature of this resourceful butterfly is that it completes the longest known migration of the insect each year. https://www.pnas.org/content/118/26/e2102762118 It can travel between 12,000 and 14,000 km round trip between Africa and Europe. During its journey, Belle-Dame must cross the Sahara Desert as well as the Mediterranean, an feat for an insect with a wingspan of 6 cm.
The unusual migration to Belle-dame is all the more interesting because it occurs over several generations. The butterfly is about two weeks old, and one individual is biologically unable to make the flight all at once. The entire annual circle is divided between 6 and 8 generations. In general, these migrations are quite irregular because they depend on the climate. If the weather is bad, the butterflies do not migrate as they should. Perhaps the formation of winds plays an essential role in their movements. From year to year, the number of belles in Europe can be multiplied by 100.
Migration across the continent
In order to understand the fluctuations of the population of Belle-dame, scientists began to pay attention to where they spend the winter. By comparing the number of individuals with climatic and ecological data in Africa, the researchers established the link between sub-Saharan winter rains and butterfly abundance. The sub-Saharan rain is indeed the root of the growth of native plants, and is an essential food source for the larvae. Belles must feed their larvae with the leaves of the plants, but the adults must also have nectar at their disposal during their long journey. If this vegetation was absent in the savannah in winter and in North Africa in the spring, the number of butterflies able to migrate would be much less.
Climate change benefits Les Belles-dames in some way. Since their number is very unstable over the years, these butterflies have few parasites and predators. To ensure its survival, the animal must already possess a certain number of resources, which is not the case for potential predators of the Belle-dame. Some researchers even suspect that the Bell ladies use their migration in part to avoid predation.
article Science It reminds us how all regions and ecosystems are interconnected. A change in weather at one point on the planet affects not only the region in question, but also other regions of the world. Therefore, the consequences of climate change are complex and difficult to predict. Migratory species are particularly vulnerable to the global and local effects of climate change. That is why it is important to focus on their movements in order to take concrete action in favor of their preservation.
article Science It reminds us of how all regions and ecosystems are interconnected. A change in weather at one point on the planet affects not only the region in question, but also other regions of the world. Therefore, the consequences of climate change are complex and difficult to predict. Migratory species are particularly vulnerable to the global and local effects of climate change. That is why it is important to focus on their movements in order to take concrete action in favor of their preservation.
>> To read also: “How do migratory birds decide to go?”