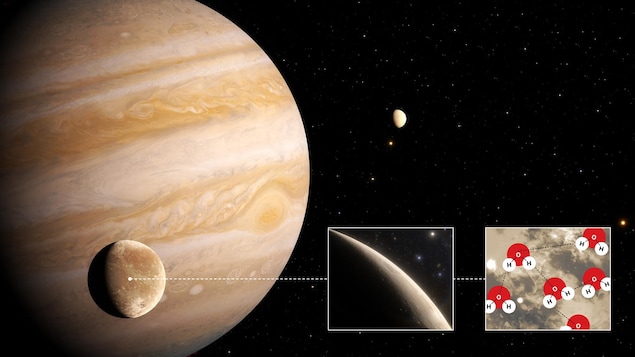
To prove the presence of this water vapor, American and European scientists re-examined data that Hubble had collected over the past two decades.
Their work is published in the magazine natural astronomy (A new window) (in English), showed that this water vapor is formed when ice sublimes on the moon’s surface, that is, it changes from a solid to a gaseous state.
Ganymede 101
- This moon is the largest natural moon of Jupiter, but also the largest in the solar system.
- With a diameter of 5,268 kilometers, it exceeds the diameter of Mercury by 8% and the diameter of Titan, the largest of Saturn’s moons, by 2%.
- It will consist of rocky material and water, the latter being mainly in the form of ice.
- Studies show that it contains more water than all of the Earth’s oceans combined.
world of ice
Much of the water on Ganymede will be buried 160 kilometers below its surface.
There would be an ocean of salt water in a liquid state, trapped between two layers of ice.
Thus, the water vapor would not come from the evaporation of this frozen ocean, but from the surface where charged particles coming from the Sun would turn the ice into water vapor.
misinterpretation
In 1998, the imaging spectrometer installed on the Hubble telescope returned the first ultraviolet (UV) images of Ganymede. Some of these images revealed colorful streaks of electrified gas, the auroras, evidence that Ganymede has a weak magnetic field.
At that time, scientists estimated that Ganymede’s atmosphere contained atomic oxygen. However, when they reconsidered these data and correlated them with more recent data, the authors of the current study came to a different conclusion: there would be practically no atomic oxygen in its atmosphere, but more molecular oxygen going to be there.
The researchers then took a closer look at the distribution of auroras in the images to conclude that Ganymede’s surface temperature may have become warm enough at the equator around noon for its icy surface to release (or sublime) small amounts of water molecules.
In fact, the differences seen in the aurora images are directly related to where water can be expected in the moon’s atmosphere.
So far we have only observed molecular oxygen الأكسجين
, explains Lorenz Roth of the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm in a press release. This results when charged particles erode the surface of the ice. The water vapor we are now measuring comes from ice sublimation caused by the thermal escape of water vapor from hot icy regions.
Concludes.
In June 2022, the European Space Agency will launch the JUICE mission to Jupiter. The probe will arrive there in 2029 and fly repeatedly over three of Jupiter’s four Galileo satellites – Callisto, Europa and Ganymede. The probe will then be placed in orbit around Ganymede for in-depth study.
A better understanding of the Jovian system, from its inception to the emergence of habitable environments, will allow us to better understand how gas giant planets and their satellites form and evolve and can support life forms.
water steam heaters It has already been discovered in Europe. Such pillars have also been discovered on Triton Neptune and Enceladus of Saturn.